Source: Check Point Research The malware performs other activities on the device. Some of its capabilities include making calls to the C&C server number, send a list of all installed apps to the C&C, and, the most peculiar one is to display a message to the victim regarding a failed payment. Ransom Not Demanded In Bitcoins Although Lucy typically behaves like any other ransomware, what makes it unique is the way it asks payment. While the attackers behind most other ransomware demand ransom in Bitcoins, Lucy Gang asks for a payment of $500 via the victim’s credit card. It seems, through this strategy by asking payments through credit cards, the attackers can gather victim’s payment card data, which they can exploit in the future as well. Certainly, this ransomware attack reiterates the need for vigilance while installing apps on mobile phones. Users must always ensure that they only download apps from official stores and trusted developers. Moreover, users should also keep their Android devices secure by ensuring prompt updates, using a robust antivirus, and employing safe browsing habits. Let us know your thoughts in the comments.
Showing posts with label Cyber Attack. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Cyber Attack. Show all posts
Thursday, 30 April 2020
Source: Check Point Research The malware performs other activities on the device. Some of its capabilities include making calls to the C&C server number, send a list of all installed apps to the C&C, and, the most peculiar one is to display a message to the victim regarding a failed payment. Ransom Not Demanded In Bitcoins Although Lucy typically behaves like any other ransomware, what makes it unique is the way it asks payment. While the attackers behind most other ransomware demand ransom in Bitcoins, Lucy Gang asks for a payment of $500 via the victim’s credit card. It seems, through this strategy by asking payments through credit cards, the attackers can gather victim’s payment card data, which they can exploit in the future as well. Certainly, this ransomware attack reiterates the need for vigilance while installing apps on mobile phones. Users must always ensure that they only download apps from official stores and trusted developers. Moreover, users should also keep their Android devices secure by ensuring prompt updates, using a robust antivirus, and employing safe browsing habits. Let us know your thoughts in the comments.
Monday, 9 March 2020
T-Mobile has once again made it to the news owing to a security incident. One more time, T-Mobile has suffered a data breach that exposed the personal and financial information of their customers. T-Mobile is presently notifying customers affected during this incident. T-Mobile Data Breach Reportedly, T-Mobile has once again suffered a data breach affecting numerous users. While it isn’t clear how many users were affected by the breach, the extent of information exposed during the incident sounds huge. Specifically, the incident happened as a result of a malicious attack against their email vendors. As a result, the attackers could gain access to T-mobile employee email accounts that included customers’ information. The news surfaced online after the service started notifying their customers about a ‘security event’ they recently ‘shut down’. Nonetheless, they have sent these notifications differently to every customer based on the extent of information exposed. For the customers who only suffered breach of personal details, the company directed them to the PII notice of the breach. In the case of these customers, the affected information included names, addresses, phone numbers, govt. ID numbers, Social Security numbers, billing and account details, rate plans and features, and financial account data. While, to some other users, the firm forwarded another security notice addressing the breach of account information. For such customers, the exposed data includes personal details such as names, contact numbers, addresses, account numbers, billing information, rate plans and features. Whereas, their Social Security numbers and financial information remained unaffected during the incident. What Next? Following the incident, the telecom giant began notifying affected customers. Though, they assured no misuse so far of the exposed details. For users receiving the PII breach notice, T-Mobile has offered free credit monitoring and identity theft services for two-years. However, for the other subset of the affected users, the firm hasn’t offered any such compensation. This isn’t the first time that the company has suffered a security incident. In 2018, they twice made it to the news owing to data breaches. Let us know your thoughts in the comments.
Friday, 28 February 2020
Google have recently fixed numerous security bugs in their Chrome browser. These Chrome bugs include two serious vulnerabilities as well as a zero-day flaw under active exploit. Chrome Zero-Day Under Exploit Researcher Clement Lecigne of Google’s Threat Analysis Group discovered a zero-day bug in the Chrome browser under active exploit. The vulnerability, CVE-2020-6418, was a type confusion flaw in V8 – a Chrome component that processes JavaScript code. Google labeled it a high-severity flaw in their advisory, what makes it serious is its exploitation in the wild. Though, Google hasn’t shared details about how the attackers are exploiting the bug. Yet, they confirm the zero-day is under attack. Other than this zero-day, Google also revealed two other bugs in the Chrome browser. These include two high-severity bugs for which, Google hasn’t hinted of any active exploitation. One of these caught the attention of Google Project Zero’s Sergei Glazunov. Google described it as an Out of bounds memory access in streams (CVE-2020-6407). The other vulnerability caught Google’s attention after researcher André Bargull reported it. This vulnerability, an integer overflow in the ICU component, the researcher was awarded a $5000 bounty. Google Released Patches Recently, Google has patched all the three flaws and released fixes with the latest Chrome version 80.0.3987.122. As the tech giant rolls out the updates, users must ensure their devices are updated to avoid any issues. This is particularly important considering the active exploitation of the zero-day. The present zero-day marks the third major vulnerability that caught the hackers’ attention before a fix. The first of these (CVE-2019-5786) surfaced online in March 2019. The attackers exploited this use after free flaw to target Windows 7. Whereas, the second vulnerability, another use after free flaw (CVE-2019-13720), appeared online in November 2019.
The latest victim of an actively exploited zero-day vulnerability is the Taiwan-based firm ‘Zyxel’ whom manufacture networking devices. Zyxel has addressed a critical zero-day vulnerability in some of its NAS devices that could allow remote code execution. Zero-Day Vulnerability In Zyxel NAS Devices The Taiwan-based technology firm Zyxel has made it into the news owing to a serious vulnerability in its network-attached storage devices. The founder of security firm Hold Security, Alex Holden, discovered a serious zero-day vulnerability in Zyxel NAS devices. As revealed through a blog post, Holden found that exploiting this vulnerability could allow a potential attacker to execute arbitrary code. Worryingly the exploit required no user permission for code execution. The researcher also noticed active sales of the exploit code on the dark web. He found ransomware gangs interested in the working exploit code which the seller put up for $20,000. CERT/CC has confirmed the presence of the vulnerability in their advisory. Regarding the details of the bug, the advisory reads, ZyXEL NAS devices achieve authentication by using the weblogin.cgi CGI executable. This program fails to properly sanitize the username parameter that is passed to it. If the username parameter contains certain characters, it can allow command injection with the privileges of the web server that runs on the ZyXEL device. While the webserver doesn’t run with root privileges, an attacker could achieve elevated privileges by abusing the setuid utility. Hence, remote code execution with root privileges would become possible. Zyxel Patched The Flaw Upon receiving the alerts for the zero-day under attack, Zyxel worked swiftly to patch the flaw. They confirmed that the vulnerability, CVE-2020-9054, affected numerous devices including NAS326, NAS520, NAS540, and NAS542. While the patches for these are available, users of NSA210, NSA220, NSA220+, NSA221, NSA310, NSA310S, NSA320, NSA320S, NSA325, and NSA325v2 would still remain vulnerable since these devices won’t receive the updates due to end-of-support. The complete list of devices and the hotfixes is available in Zyxel’s advisory. Zyxel have recommended limiting access to vulnerable NAS devices and blocking access to the web interface as possible mitigations.
Monday, 6 January 2020
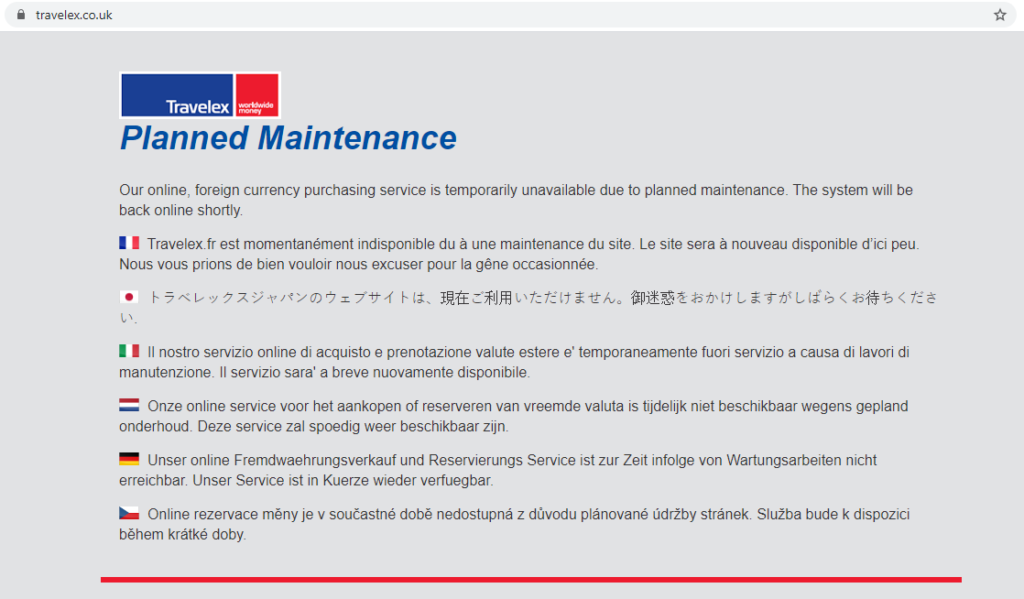
While everyone was busy on New Year’s Eve in welcoming the calendrical change, cybercriminals were busy “working”. The evidence backing this statement came from the cyber attack on foreign currency exchange Travelex. Recently, Travelex has confirmed a malware attack hit its systems, following which, its services went down. Travelex Disclosed Malware Attack Reportedly, the international foreign currency exchange service Travelex has emerged as the latest victim of a cyber attack. As experienced by users, and confirmed by the service, Travelex services went down following the malware attack. The exchange clearly defined the incident as a ‘malware’ attack. Sharing their statement in a tweet, Travelex mentioned, Travelex confirms that a software virus was discovered on New Year’s Eve which has compromised some of its services. They also confirmed the shut down of their services, which they did as a precaution. As a precautionary measure in order to protect data and prevent the spread of the virus, we immediately took all our systems offline.
Though the exchange only stated about the disruption of ‘some’ services, it actually caused huge trouble to the users. The attack potentially affected the partnering businesses as well, such as Tesco Bank.
The disruptions also caused severe problems for the users in withdrawing money.
Security Measures And Maintenance Underway After the online services of Travelex went down, the company had to manage serving customers by providing exchange manually. They also engaged cybersecurity experts to resolve the matter. However, until the time of writing this article, the Travelex website is still down.While Travelex are still striving to restore their services, they assure that the incident did not affect customers’ data. For any queries, customers can contact them via their official twitter account where they are actively responding. Before Travelex, numerous other incidents affecting different businesses also surfaced online towards the end of 2019. Some of the affected services include Poloniex cryptocurrency exchange, telemarketing firm The Heritage Company, IT service provider Synoptek, and a US Maritime facility.
Saturday, 14 September 2019
Mozilla has officially launched a new privacy-focused VPN service, called Firefox Private Network, as a browser extension that aims to encrypt your online activity and limit what websites and advertisers know about you.
Firefox Private Network service is currently in beta and available only to desktop users in the United States as part of Mozilla's recently expunged "Firefox Test Pilot" program that lets users try out new experimental features before they were officially released.
The Firefox Test Pilot program was first launched by the company three years ago but was shut down in January this year. The company now decided to bring the program back but with some changes.
Firefox Private Network is the Test Pilot program's first new project.
Like any other best VPN service, Firefox Private Network also masks your IP address from third-party online trackers and protect your sensitive information, like the website you visit and your financial information, when using public Wi-Fi.
Mozilla says its Firefox Private Network "provides a secure, encrypted path to the web to protect your connection and your personal information anywhere, and everywhere you use your Firefox browser."
Firefox Private Network also works the same way as any other VPN service.
The Firefox Private Network VPN service also encrypts and funnels every Internet browsing activity of yours through a collection of remote proxy servers, thereby masking your real location/identity and blocking third parties, including government and your ISP, from snooping on your connection.
The actual proxy servers for the Firefox Private Network extension is provided by Cloudflare, the company that offers one of the biggest and fastest CDN, DNS and DDoS protection services.
For those concerned about the data collection by Cloudflare, Mozilla promises "strong privacy controls" to limit what data Cloudflare may collect and for how long it may store that data.
Firefox Private Network currently works only on desktops but is believed to be made available for mobile users as well, once the VPN exits beta.
Although the Firefox Private Network service is currently free, Mozilla hinted that the company is exploring possible pricing options for the service in the future to keep it self-sustainable.
For now, if you have a Firefox account and reside in the United States, you can test the Firefox VPN service for free by signing up on the Firefox Private Network website.
Once installed on your desktop, the Firefox Private Network extension will add a toggle on the toolbar of your Firefox web browser so you can easily turn it on or off at any time.
Firefox Private Network service is currently in beta and available only to desktop users in the United States as part of Mozilla's recently expunged "Firefox Test Pilot" program that lets users try out new experimental features before they were officially released.
The Firefox Test Pilot program was first launched by the company three years ago but was shut down in January this year. The company now decided to bring the program back but with some changes.
"The difference with the newly relaunched Test Pilot program is that these products and services may be outside the Firefox browser, and will be far more polished, and just one step shy of general public release," said Marissa Wood, vice president of product at Mozilla.
Firefox Private Network is the Test Pilot program's first new project.
Firefox Private Network — Mozilla's VPN Service
Like any other best VPN service, Firefox Private Network also masks your IP address from third-party online trackers and protect your sensitive information, like the website you visit and your financial information, when using public Wi-Fi.
Mozilla says its Firefox Private Network "provides a secure, encrypted path to the web to protect your connection and your personal information anywhere, and everywhere you use your Firefox browser."
Firefox Private Network also works the same way as any other VPN service.
The Firefox Private Network VPN service also encrypts and funnels every Internet browsing activity of yours through a collection of remote proxy servers, thereby masking your real location/identity and blocking third parties, including government and your ISP, from snooping on your connection.
The actual proxy servers for the Firefox Private Network extension is provided by Cloudflare, the company that offers one of the biggest and fastest CDN, DNS and DDoS protection services.
For those concerned about the data collection by Cloudflare, Mozilla promises "strong privacy controls" to limit what data Cloudflare may collect and for how long it may store that data.
"Cloudflare only observes a limited amount of data about the HTTP/HTTPS requests that are sent to the Cloudflare proxy via browsers with an active Mozilla extension," Cloudflare says.
"When requests are sent to the Cloudflare proxy, Cloudflare will observe your IP address, the IP address for the Internet property you are accessing, source port, destination port, timestamp and a token provided by Mozilla that indicates that you are a Firefox Private Network user (together, "Proxy Data"). All Proxy Data will be deleted within 24 hours."
How To Sign Up For Firefox VPN Service
Firefox Private Network currently works only on desktops but is believed to be made available for mobile users as well, once the VPN exits beta.
Although the Firefox Private Network service is currently free, Mozilla hinted that the company is exploring possible pricing options for the service in the future to keep it self-sustainable.
For now, if you have a Firefox account and reside in the United States, you can test the Firefox VPN service for free by signing up on the Firefox Private Network website.
Once installed on your desktop, the Firefox Private Network extension will add a toggle on the toolbar of your Firefox web browser so you can easily turn it on or off at any time.
Immediately after Mozilla announced its plan to soon enable 'DNS over HTTPS'
(DoH) by default for Firefox users in the United States, Google today
says it is planning an experiment with the privacy-focused technology in
its upcoming Chrome 78.
Under development since 2017, 'DNS over HTTPS' performs DNS lookups—finding the server IP address of a certain domain name—over an encrypted HTTPS connection to a DNS server, rather than sending DNS queries in plaintext.
The protocol that sends DNS queries over secure HTTPS connections has specifically been designed to prevent miscreants from interfering with domain name lookups, eventually stopping network observers, including your ISPs and attackers, from figuring out what sites you visit.
Though the privacy-focused technology is also helpful in preventing attackers from redirecting unsuspecting visitors to phishing and malware sites, DNS over HTTPS could also bring its own new challenges to the enterprise security solutions by making it difficult to monitor network traffic for malicious activities.
For the same reason, two months ago, the UK Internet Services Providers' Association (ISPA) nominated Mozilla for "Internet villain of the year" award after the company added support for DoH protocol in its Firefox browser that breaks DNS-based content filters.
However, it should be noted that Firefox by default sets DoH server to Cloudflare and the setting needs to be changed manually, for which Mozilla has been criticized, whereas Google's implementation only upgrades to the equivalent DoH service from the same provider that a user is using.
In a blog post published today, Google said the company will add its implementation of 'DNS over HTTPS' to the upcoming Chrome 78, which is due for beta release in the next two weeks, and will enable the feature for a fraction of users as an early-experiment,
The experimental feature will automatically upgrade the DNS provider to the equivalent DoH service from the same provider if the user's current DNS provider is part of the list of known DoH-compatible providers. If not in the list, Chrome will continue to operate as it does today.
Chrome 78 users who want to manually opt-in or opt-out of the experiment can change the flag settings at chrome://flags/#dns-over-https.
Google says it has selected some DNS providers for "their strong stance on security and privacy, as well as the readiness of their DoH services" and their agreement to participate in the test. The list of providers currently include:
The experiment will run on all platforms for Chrome 78 users except Linux and iOS, with the goals to validate the company's "implementation and to evaluate the performance impact."
On Android 9 and later, if users have set a DNS-over-TLS (DoT) provider in the private DNS settings, Chrome may attempt to utilize DoH instead, but if an error occurred, the browser would fall back to the DoT setting.
For those unaware, though DoH and DoT are separate standards for encrypting DNS queries, the concept of both is the same.
What're your thoughts on Google's experiment of implementing DoH? Let us know in the comment section below.
Under development since 2017, 'DNS over HTTPS' performs DNS lookups—finding the server IP address of a certain domain name—over an encrypted HTTPS connection to a DNS server, rather than sending DNS queries in plaintext.
The protocol that sends DNS queries over secure HTTPS connections has specifically been designed to prevent miscreants from interfering with domain name lookups, eventually stopping network observers, including your ISPs and attackers, from figuring out what sites you visit.
Though the privacy-focused technology is also helpful in preventing attackers from redirecting unsuspecting visitors to phishing and malware sites, DNS over HTTPS could also bring its own new challenges to the enterprise security solutions by making it difficult to monitor network traffic for malicious activities.
For the same reason, two months ago, the UK Internet Services Providers' Association (ISPA) nominated Mozilla for "Internet villain of the year" award after the company added support for DoH protocol in its Firefox browser that breaks DNS-based content filters.
However, it should be noted that Firefox by default sets DoH server to Cloudflare and the setting needs to be changed manually, for which Mozilla has been criticized, whereas Google's implementation only upgrades to the equivalent DoH service from the same provider that a user is using.
Enabling 'DNS over HTTPS' in Chrome 78
In a blog post published today, Google said the company will add its implementation of 'DNS over HTTPS' to the upcoming Chrome 78, which is due for beta release in the next two weeks, and will enable the feature for a fraction of users as an early-experiment,
The experimental feature will automatically upgrade the DNS provider to the equivalent DoH service from the same provider if the user's current DNS provider is part of the list of known DoH-compatible providers. If not in the list, Chrome will continue to operate as it does today.
"In other words, this would upgrade the protocol used for DNS resolution while keeping the user's DNS provider unchanged. It's also important to note that DNS over HTTPS does not preclude its operator from offering features such as family-safe filtering," Google says.
Chrome 78 users who want to manually opt-in or opt-out of the experiment can change the flag settings at chrome://flags/#dns-over-https.
Chrome Compatible' DNS over HTTPS' Providers
Google says it has selected some DNS providers for "their strong stance on security and privacy, as well as the readiness of their DoH services" and their agreement to participate in the test. The list of providers currently include:
- Cleanbrowsing
- Cloudflare
- DNS.SB
- OpenDNS
- Quad9
The experiment will run on all platforms for Chrome 78 users except Linux and iOS, with the goals to validate the company's "implementation and to evaluate the performance impact."
On Android 9 and later, if users have set a DNS-over-TLS (DoT) provider in the private DNS settings, Chrome may attempt to utilize DoH instead, but if an error occurred, the browser would fall back to the DoT setting.
For those unaware, though DoH and DoT are separate standards for encrypting DNS queries, the concept of both is the same.
What're your thoughts on Google's experiment of implementing DoH? Let us know in the comment section below.
Unlike previous side-channel vulnerabilities disclosed in Intel CPUs,
researchers have discovered a new flaw that can be exploited remotely
over the network without requiring an attacker to have physical access
or any malware installed on a targeted computer.
Dubbed NetCAT, short for Network Cache ATtack, the new network-based side-channel vulnerability could allow a remote attacker to sniff out sensitive data, such as someone's SSH password, from Intel's CPU cache.
Discovered by a team of security researchers from the Vrije University in Amsterdam, the vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2019-11184, resides in a performance optimization feature called Intel's DDIO—short for Data-Direct I/O—which by design grants network devices and other peripherals access to the CPU cache.
The DDIO comes enabled by default on all Intel server-grade processors since 2012, including Intel Xeon E5, E7 and SP families.
According to the researchers [paper], NetCAT attack works similar to Throwhammer by solely sending specially crafted network packets to a targeted computer that has Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) feature enabled.
RDMA enables attackers to spy on remote server-side peripherals such as network cards and observe the timing difference between a network packet that is served from the remote processor's cache versus a packet served from memory.
Here the idea is to perform a keystroke timing analysis to recover words typed by a victim using a machine learning algorithm against the time information.
"Compared to a native local attacker, NetCAT's attack from across the network only reduces the accuracy of the discovered keystrokes on average by 11.7% by discovering inter-arrival of SSH packets with a true positive rate of 85%."
The VUSec team has also published a video, as shown above, demonstrating a method for spying on SSH sessions in real-time with nothing but a shared server.
NetCAT becomes the new side-channel vulnerability joined the list of other dangerous side-channel vulnerabilities discovered in the past year, including Meltdown and Spectre, TLBleed, Foreshadow, SWAPGS, and PortSmash.
In its advisory, Intel has acknowledged the issue and recommended users to either completely disable DDIO or at least RDMA to make such attacks more difficult, or otherwise suggested to limit direct access to the servers from untrusted networks.
The company assigned the NetCAT vulnerability a "low" severity rating, describing it as a partial information disclosure issue, and awarded a bounty to the VUSec team for the responsible disclosure.
Dubbed NetCAT, short for Network Cache ATtack, the new network-based side-channel vulnerability could allow a remote attacker to sniff out sensitive data, such as someone's SSH password, from Intel's CPU cache.
Discovered by a team of security researchers from the Vrije University in Amsterdam, the vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2019-11184, resides in a performance optimization feature called Intel's DDIO—short for Data-Direct I/O—which by design grants network devices and other peripherals access to the CPU cache.
The DDIO comes enabled by default on all Intel server-grade processors since 2012, including Intel Xeon E5, E7 and SP families.
According to the researchers [paper], NetCAT attack works similar to Throwhammer by solely sending specially crafted network packets to a targeted computer that has Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) feature enabled.
RDMA enables attackers to spy on remote server-side peripherals such as network cards and observe the timing difference between a network packet that is served from the remote processor's cache versus a packet served from memory.
Here the idea is to perform a keystroke timing analysis to recover words typed by a victim using a machine learning algorithm against the time information.
"In an interactive SSH session, every time you press a key, network packets are being directly transmitted. As a result, every time a victim you type a character inside an encrypted SSH session on your console, NetCAT can leak the timing of the event by leaking the arrival time of the corresponding network packet," explains the VUSec team.
"Now, humans have distinct typing patterns. For example, typing's' right after 'a' is faster than typing 'g' after's.' As a result, NetCAT can operate statical analysis of the inter-arrival timings of packets in what is known as a keystroke timing attack to leak what you type in your private SSH session."
"Compared to a native local attacker, NetCAT's attack from across the network only reduces the accuracy of the discovered keystrokes on average by 11.7% by discovering inter-arrival of SSH packets with a true positive rate of 85%."
The VUSec team has also published a video, as shown above, demonstrating a method for spying on SSH sessions in real-time with nothing but a shared server.
NetCAT becomes the new side-channel vulnerability joined the list of other dangerous side-channel vulnerabilities discovered in the past year, including Meltdown and Spectre, TLBleed, Foreshadow, SWAPGS, and PortSmash.
In its advisory, Intel has acknowledged the issue and recommended users to either completely disable DDIO or at least RDMA to make such attacks more difficult, or otherwise suggested to limit direct access to the servers from untrusted networks.
The company assigned the NetCAT vulnerability a "low" severity rating, describing it as a partial information disclosure issue, and awarded a bounty to the VUSec team for the responsible disclosure.
Estonian based web security startup WebARX, the company who is also
behind open-source plugin vulnerability scanner WPBullet and
soon-to-be-released bug bounty platform plugbounty.com, has a big vision for a safer web.
It built a defensive core for websites which is embedded deep inside the company's DNA as even ARX in their name refers to the citadel (the core fortified area of a town or city) in Latin.
WebARX—web application security platform—allows web developers and digital agencies to get advanced website security integrated with every site and makes it more effective and less time-consuming to manage security across multiple websites.
You can find reviews such as "WebARX - the Swiss army knife that secures my websites!", "The security software that I use every day," "Many Promise - WebARX Delivers" from their Trustpilot page, so where is all that coming from?
WebARX is solving a very specific problem—reducing the security risk from third-party components within web applications, or as its website states, "Protect websites from plugin vulnerabilities."
In fact, the latest studies show that 98% of security vulnerabilities within the WordPress ecosystem (running 35% of the websites online) are related to plugins, which are intended to expand the functionality and features of a website.
Additionally, by contributing to the open-source with WPBullet, the company is also planning to release the first open-source plugin bug bounty platform plugbounty.com, which is released in few weeks.
Lately, WebARX has gained a lot of popularity for its security platform. According to many, it's one of the most advanced solutions for modern websites that are built on WordPress or any other PHP based content management system.
It takes less than a minute to add a site to the portal and activate monitoring and firewall.
WebARX protects sites from malicious traffic, unwanted bot requests, and prevents OWASP TOP 10 vulnerability exploitation.
As a managed service, WebARX is actively keeping its firewall up to date with the latest threats. Virtual patches are applied automatically to prevent software specific vulnerabilities mostly found within components such as plugins and themes.
The firewall has its benefits from running on the end-point and being component agnostic.
Since WebARX is running on the site, it can't be bypassed the way DNS firewalls are often bypassed (when the IP to the server is leaked by abusing DNS history or when the server is not configured correctly allowing traffic from sources other than what is coming through the firewall).
With WebARX you have the freedom to create an unlimited number of custom firewall rules (match anything within HTTP protocol).
You can analyze and control the firewall among all your sites from the central cloud-based dashboard.
WordPress, as the most popular content management system, has clearly received a lot of attention. According to some statistics, it runs already more than 35% of the websites.
Attention is not always positive, and this has made WordPress a very attractive target for attackers.
Hundreds of thousands of websites are being abused to redirect traffic, host malware, send out spam and sites are even used as slaves in botnets.
Victims are not chosen; most of the attacks are automated, which targets the software, not the company or the people behind the website itself.
WordPress security is an active topic. Just a week ago, a critical 'Backdoor Attack' warning was issued for 60 million WordPress users via Forbes.
"A must for WordPress sites!" as one of its Trustpilot review states, WebARX has already gone a long way to ultimately become the only WordPress security solution you need.
It's always good to keep the number of components/plugins low while having all the security and hardening options available for every site.
Some of the options WebARX includes:
WebARX is currently celebrating its birthday, and a 50% discount is offered for a limited time.
It built a defensive core for websites which is embedded deep inside the company's DNA as even ARX in their name refers to the citadel (the core fortified area of a town or city) in Latin.
WebARX—web application security platform—allows web developers and digital agencies to get advanced website security integrated with every site and makes it more effective and less time-consuming to manage security across multiple websites.
You can find reviews such as "WebARX - the Swiss army knife that secures my websites!", "The security software that I use every day," "Many Promise - WebARX Delivers" from their Trustpilot page, so where is all that coming from?
Serious Team With A Unique Focus
WebARX is solving a very specific problem—reducing the security risk from third-party components within web applications, or as its website states, "Protect websites from plugin vulnerabilities."
In fact, the latest studies show that 98% of security vulnerabilities within the WordPress ecosystem (running 35% of the websites online) are related to plugins, which are intended to expand the functionality and features of a website.
Additionally, by contributing to the open-source with WPBullet, the company is also planning to release the first open-source plugin bug bounty platform plugbounty.com, which is released in few weeks.
Advanced Protection For Any PHP App Made Simple and Accessible
Lately, WebARX has gained a lot of popularity for its security platform. According to many, it's one of the most advanced solutions for modern websites that are built on WordPress or any other PHP based content management system.
It takes less than a minute to add a site to the portal and activate monitoring and firewall.
WebARX protects sites from malicious traffic, unwanted bot requests, and prevents OWASP TOP 10 vulnerability exploitation.
As a managed service, WebARX is actively keeping its firewall up to date with the latest threats. Virtual patches are applied automatically to prevent software specific vulnerabilities mostly found within components such as plugins and themes.
The firewall has its benefits from running on the end-point and being component agnostic.
Since WebARX is running on the site, it can't be bypassed the way DNS firewalls are often bypassed (when the IP to the server is leaked by abusing DNS history or when the server is not configured correctly allowing traffic from sources other than what is coming through the firewall).
With WebARX you have the freedom to create an unlimited number of custom firewall rules (match anything within HTTP protocol).
You can analyze and control the firewall among all your sites from the central cloud-based dashboard.
WordPress In the Center of Attention
WordPress, as the most popular content management system, has clearly received a lot of attention. According to some statistics, it runs already more than 35% of the websites.
Attention is not always positive, and this has made WordPress a very attractive target for attackers.
Hundreds of thousands of websites are being abused to redirect traffic, host malware, send out spam and sites are even used as slaves in botnets.
Victims are not chosen; most of the attacks are automated, which targets the software, not the company or the people behind the website itself.
WordPress security is an active topic. Just a week ago, a critical 'Backdoor Attack' warning was issued for 60 million WordPress users via Forbes.
WebARX is the All-in-One Solution For WordPress Sites
"A must for WordPress sites!" as one of its Trustpilot review states, WebARX has already gone a long way to ultimately become the only WordPress security solution you need.
It's always good to keep the number of components/plugins low while having all the security and hardening options available for every site.
Some of the options WebARX includes:
- WAF with virtual patches and an unlimited number of custom rules.
- Advanced firewall management and analytics.
- Central, easy to use cloud-based security portal.
- Up-time, Blacklist, Domain/SSL expiration, and plugin vulnerability monitoring.
- 2FA for any site and each user.
- ReCAPTCHA implementation for forms.
- Brute-force/XML-RPC protection.
- Automatic off-site backups to Google Drive.
- Customizable cookie notice bar.
- User activity logging.
- Cloud-based plugin management (remote updating).
- Cloud-based hardening.
- Multi-site support.
- And much more…
WebARX is currently celebrating its birthday, and a 50% discount is offered for a limited time.
Saturday, 31 August 2019
Whilst you would expect cybersecurity and IT firms to serve customers with adequate online security measures. However, these firms themselves remain vulnerable to various security threats too. Recently, the cybersecurity firm Imperva has disclosed a security breach that affected customers of its Cloud WAF. Imperva Revealed Security Breach In a recent security notice, the popular cybersecurity firm Imperva has revealed a security breach. The incident impacted customers of its Cloud WAF product previously known as ‘Incapsula’. As disclosed, the company learned of the breach recently from a third-party. They discovered the incident on August 20, 2019, where they found the exposure of data of some of the customers. The company found that the incident impacted a database through September 15, 2019. The leaked or exposed information from the database includes email addresses, hashed and salted passwords. For a subset of customers, exposed details also included customer-provided SSL certificates and API keys. The company assured that the impact of the incident remained confined to the Cloud WAF product only. Security Measures Taken Upon noticing the breach, Imperva began working towards implementing appropriate security measures. These steps include engaging forensic experts and global regulatory agencies, activating internal data security response team, and implementing forced password rotations in Cloud WAF. In addition, they have also informed customers affected during the incident regarding the breach. They also advise customers to take necessary steps to stay protected. Some of the security best practices Imperva advised to all users include resetting Cloud WAF user passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, enabling Single Sign-On (SSO), uploading new SSL certificates and resetting API keys. Recently, a web hosting company Hostinger has also confessed of a breach. The incident allegedly affected 14 million customers, exposing the victims’ personal information and hashed passwords. Let us know your thoughts in the comments.
Monday, 13 May 2019
A critical security vulnerability in ISPsystem software put nearly 10,000 installations at risk. Exploiting the vulnerability could allow an attacker to hijack a web session of another logged-in user. The vulnerability allegedly affected all ISPsystem products.
Critical ISPsystem Software Vulnerability Discovered
The Check Point Research team have discovered a critical security vulnerability in ISPsystem software. As per their findings, the vulnerability could allow an attacker to hijack a web session of logged-in users. This could subsequently allow the attacker to compromise websites and virtual machines, and pilfer data.
Stating about their discovery in their blog post, they explained that the vulnerability threatened the integrity of all ISPsystem products including ISPmanager, DCImanager, VMmanager, BILLmanager, IPmanager, COREmanager, and DNSmanager.
As elaborated in their post, the server used to set a session cookie for an authenticated user. A potential attacker could hijack a logged-in web session by picking up the correct 6-byte HEX encoded string value of the cookie via a session cookie generator algorithm.
ISPsystem Fixed The Bug
Upon finding the vulnerability in the ISPsystem software, researchers quickly notified the officials regarding the matter. They confirm that ISPsystem support quickly responded to their report and fixed the bug.
So, the vulnerability that affected roughly 11,000 ISPsystem installations has been patched with the software version 5.178.2. While the vendors already released the fixin November 2018, anyone running the software versions older than 5.178.2 must ensure updating to the higher versions to stay protected from possible cyber threats.
ISPsystem is a comprehensive user-friendly software offering various functionalities. It facilitates in managing websites and web-server, VPS (virtual private servers), dedicated servers, billing and payment services. As stated on their website, ISPsystem has its clients in around 150 countries. Some of the popular hosting providers using their products include King Servers, 1Cloud, and Ru-Center.
Take your time to comment on this article.
Friday, 3 May 2019
A newly discovered Qualcomm chip vulnerability threatens the security of Android smartphones. Exploiting this flaw could allow an attacker to extract private keys and passwords from the Qualcomm secure keystore.
Qualcomm Chip Vulnerability Discovered
Researchers from NCC Group have recently found a Qualcomm chip vulnerability threatening Android phones. They have shared the details about their findings in a separate report on their site. They shared the technical aspects of their discovery in their research paper.
Specifically they found a side-channel attack that could allow an attacker to extract data from the Qualcomm secure keystore. This hardware-backed keystore is a feature on most modern Android phones which allows developers to protect their cryptographic keys.
According to their research, the problem lies at the “Elliptic curve point multiplication in Qualcomm’s QSEE code.” Ideally, the Qualcomm’ ECDSA implementation (a NIST-standardized digital signature algorithm) should not leak the stored sensitive data. However, the researchers demonstrated a side-channel attack on the Qualcomm’s TEE (Trusted Execution Environment) via Cachegrab (an open-source attack tool) that revealed the data. They demonstrated a successful extraction of 256-bit private key of the Nexus 5X.
Qualcomm Patched The Flaw
As stated in their blog post, the researchers contacted Qualcomm and informed them of the flaw in March 2018. Qualcomm then began working on a fix, and rolled-out a patch for the customers in October 2018. They have considered it a critical security flaw, assigning it CVE-2018-11976.
After discussion with the vendor, the researchers shared the report publicly in April 2019 with some recommendations for the developers.
“Android developers who use the keystore in their applications can also take advantage of the user authentication requirements and key attestation offered by the keystore. These defense-in-depth mitigations increase the complexity of compromising keystore keys, making difficult-to-perform side-channel attacks even more challenging to pull off.”
Take your time to comment on this article.
Wednesday, 24 April 2019
Once again, a healthcare service has suffered a cyber attack threatening the security of its users. This time, the victim is an app for physicians – EmCare. As reported by the company itself, a cyber attack resulted in an EmCare data breach exposing information of some patients and employees.
EmCare Data Breach Exposed Personal And Clinical Data
A physician-service firm EmCare Inc. recently disclosed its encounter with a cyber attack. The EmCare data breach exposed explicit personal details of the staff and the patients. Also, it compromised the medical information of some patients.
As stated in their security notice, EmCare discovered unauthorized access to the email accounts of their employees. Upon digging out further, the authorities could identify a breach. Regarding the patients possibly affected the breach, EmCare stated,
“Patients impacted by this incident may have received medical care from a clinician employed by or engaged with an affiliate of EmCare. These services may have been provided in an Emergency Department or as inpatient services in a hospital.”
They originally identified on February 19, 2019, the email accounts affected by the suspicious intrusion exposed personal details of the patients and the staff. Hence, the breached data include individual’s names, birth dates, age, and clinical data of some patients. For some cases, the exposed details also included social security numbers and driver’s license numbers.
While the company has not stated any precise number of those affected, Bloomberg reported 60,000 affected individuals. Of these, 31,000 records belong to the patients. Bloomberg reported this data quoting the information stated in EmCare’s email.
EmCare Takes Security Measures
After noticing the breach, the firm started investigations to reveal the details. They now confirm no misuse of breach data.
“There is no evidence to suggest that the information has been misused, or that anyone will attempt to misuse the information. In addition, EmCare is not aware of any individual who has been impacted by fraud or identity theft as a result and does not know if any personal information was actually obtained by an unauthorized party.”
The company has also offered to arrange membership to Experian’s IdentityWorks for identity protection and credit monitoring services. This offer applies to all the individuals whose Social Security and license numbers were exposed in the incident.
EmCare has also notified all affected individuals of the data breach via individual emails.
Earlier this month, a Canadian firm Natural Health Services exposed personal information of medical marijuana patients in a data breach.
Let us know your thoughts in the comments section.
Thursday, 11 April 2019
Another Microsoft Office vulnerability has surfaced online that threatens most MS Office users. This time, the flaw appears in MS Word that allows potential attackers to bypass all security measures upon exploit. However, the vendors refused to patch this Microsoft Word bug despite knowing about it for long.
Microsoft Word Bug Under Active Exploits
Researchers from Mimecast Research Labs have uncovered active exploits of a Microsoft Word bug. They found that the vulnerability allows attackers to evade all security measures such as antimalware on the target system.
The flaw basically exists in the way of handling Integer Overflow errors by Microsoft Word in OLE file format. Together with another memory corruption vulnerability (CVE-2017-11882) patched earlier, the researchers found hackers actively exploiting the vulnerability to take over systems. The group of hackers allegedly belongs to Serbia. They use specially crafted Microsoft Word documents to exploit the OLE vulnerability, thereby bypassing all security measures. As stated by Mimecast,
“The group was able to exploit this bug to circumvent many security solutions designed to protect data from infestation, including leading sandbox and anti-malware technologies.”
In the case analyzed by Mimecast, hackers allegedly dropped JACKSBOT malware to the target systems. This malware allows the attackers to gain complete access to the victim machine. About the malware, the researchers state,
“Malware code reveals that it is capable of visiting URLs, creating files and/or folders, running shell commands, and executing and ending programs. It can also steal information by logging keystrokes and mouse events.”
The researchers have elaborated about the technicalities of the exploit in their report.
No Patch From Microsoft
Upon discovering the exploit, Mimecast reached Microsoft, informing them of the flaw. While Microsoft acknowledged their report, they allegedly refused to release a fix for now.
“Microsoft acknowledged it was unintended behavior, but declined to release a security patch at this time, as the issue on its own does not result in memory corruption or code execution. The issue may be fixed at a later date.”
Mimecast discovered and reported the vulnerability to Microsoft in May 2018. However, the flaw still persists allowing the hackers active exploitation.
Thursday, 15 November 2018
In September, Adobe patched numerous critical vulnerabilities in ColdFusion. However, a couple of weeks after Adobe released the patches, researchers noticed active exploitation of Adobe ColdFusion vulnerability in the wild. Reportedly, they have identified a Chinese APT group behind the exploit. The group has actively attacked unpatched servers.
Adobe ColdFusion Vulnerability Exploited In The Wild
Researchers at Volexity discovered active exploitation of Adobe ColdFusion vulnerability. Although Adobe already patched the vulnerability, it seems the hackers took advantage of the details published in Adobe’s advisory, after which they began exploiting the flaw.
The vulnerability exploited in this case is an unrestricted file upload bug (CVE-2018-15961). Exploiting this bug could lead to arbitrary code execution – and this is what the hackers did. The attackers belonged to a Chinese APT group who carried out direct uploads of a China Chopper webshell to vulnerable ColdFusion servers.
Regarding how they managed to conduct the attack, Volexity stated in their report,
“The vulnerability is easily exploited through a simple HTTP POST request to the file upload.cfm, which is not restricted and does not require any authentication.”
According to Volexity, the vulnerability arose when Adobe switched the ColdFusion WYSIWYG editor from FCKEditor to CKEditor. Though Adobe already patched it, yet the hackers didn’t miss the chance to exploit the bug on unpatched servers. They simply noticed that the CKEditor didn’t include .jsp file extension among the restricted file upload extensions. They also accessed the “path” form variable and identified an issue related to directory modification through which they could alter the directory. Therefore, nothing could seemingly hinder their malicious activities.
Reportedly, Volexity identified various unpatched ColdFusion servers belonging to different institutions that appeared compromised. Volexity then informed Adobe about their findings who were unaware of any exploits.
Update Your Software ASAP!
The prime reason behind the success of the hacktivist group involved in these attacks is the failure to download patched software. The attackers looked for unpatched servers to carry out their malicious activities. So, to ensure adequate protection against these attacks, ColdFusion users must ensure downloading the patched updates. Moreover, the researchers also recommend limiting the access to ColdFusion servers to only a few approved IP addresses.
Let us know your thoughts in the comments section.
Friday, 26 October 2018
Continuing with the trail of crypto hacks, another crypto exchange has become a victim of cyber attack. This time, it is Trade.io – a Swiss-based crypto exchange that just lost $7.5 million worth of crypto TIO tokens. The hackers managed to steal the tokens by hacking a cold wallet. The incident did not affect the users since the hacked Trade.io cold wallet belonging to the company and the liquidity pool was therefore not affected.
Trade.io Cold Wallet Hacked By Unknown Attackers
As disclosed recently on the exchange’s website, the Switzerland based crypto exchange, Trade.io endured a cyber attack. Allegedly, the hackers stole 50 million TIO tokens by hacking a Trade.io cold wallet.
The exchange noticed the breach on October 20, 2018, after observing a large transaction from one of its cold wallets reserved for liquidity pool. By the time they could take some action, they noticed massive token transfer to other exchanges. Nonetheless, the Trade.io acted promptly, and notified the two exchanges, KuCoin and Bancor, to halt trading TIO. The exchanges responded promptly and trading of TIO tokens stopped.
After the team began investigating the matter, the found that the hackers allegedly pilfered 50 million TIO tokens worth $11 million at the time of hack. However, within a few hours after the incident, the value of the lost tokens dropped to $7.5 million.
Trade.io Decided Hard Fork
The Trade.io officials confirm that the hack did not affect the exchange’s usual operations. Nor did it affect the customers or the Trade.io liquidity pool. The hackers could only access one of the Trade.io cold wallets hack the tokens. As stated in their announcement,
“At no point was the trade.io exchange or liquidity pool accessed or affected, and both remain operational. The breach was limited to one particular hardware wallet that was purchased directly from the manufacturer. Consequently, no customer accounts were directly affected, or customer funds lost.”
Besides confirming the system’s security, they also rule out any chances of the involvement of internal actors in the theft. Nonetheless, they still look forward to eliminating any chances of losses by a hard fork.
“As a result of the incident, trade.io Management has decided to fork TIO. The name of the forked token will be Trade Token X with the ticker TIOx, similar to TIO it will be an ERC-20 token.”
They said that they will reveal more details about the forked token soon.
Let us know your thoughts in the comments below.